sThe first case of monkeypox in a human was reported in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Since then, there have been many monkeypox outbreaks, but they have been self-limiting, with chains of human transmission ending without establishing epidemics. The current outbreak, however, is different. There is more human-to-human transmission, and it is over a much broader geographical area.
In mere weeks, monkeypox has spread to 37 non-endemic countries, with over 2,600 cases. So, what is likely to happen to monkeypox in the following weeks and months?
There are huge gaps in what we know about monkeypox, but combining what we do know with a history of other infectious diseases makes it possible to analyse likely future scenarios.
The four scenarios below are based on the following knowledge: the average number of people an infected person is likely to infect (assuming they have not been vaccinated against the virus or have had the disease before) is 2.13. This is called the basic reproduction number, or R. Herd immunity — the point at which enough people have immunity such that disease transmission can’t be sustained — is 53 per cent (corresponding to this value of R). And the incubation period, the time from catching the virus to the appearance of symptoms, is between five and 21 days.
Scenario one: self-limiting outbreak
The 2022 epidemic appears to have started as a super-spreader event involving a network of predominantly men who have sex with men.
But until the current outbreak it was assumed that the relatively low human-to-human transmissibility of the virus makes it unlikely for the virus to spread outside the initial community.
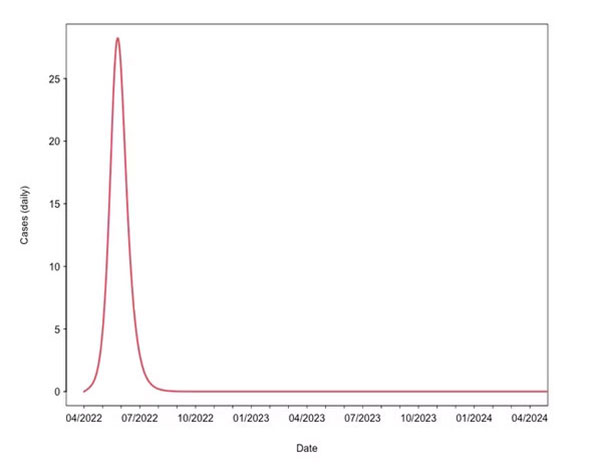
In this scenario, the outbreak ends quickly once the population at risk becomes immune and herd immunity is reached locally. In the past, many people had some immunity (called “cross-immunity”) from the smallpox mass vaccination programs of the late 20th century. So the effective reproduction number, R, can be close to or even lower than one, and the transmission will soon stop.
Behavioural changes can reduce the number R even more. For example, the ring vaccination can form a “firebreak,” further reducing the susceptible population. Similar previous epidemics include the SARS outbreak in 2002 to 2004, when quick intervention stopped the disease from spreading.
Scenario two: all population
The continuing spread of monkeypox in May and June 2022 suggests that the virus is moving beyond the original network.
The size of the outbreak is already well beyond the most prominent 2017 to 2019 outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which numbered 760. It is possible that large gatherings, including raves and festivals, have created new transmission clusters.
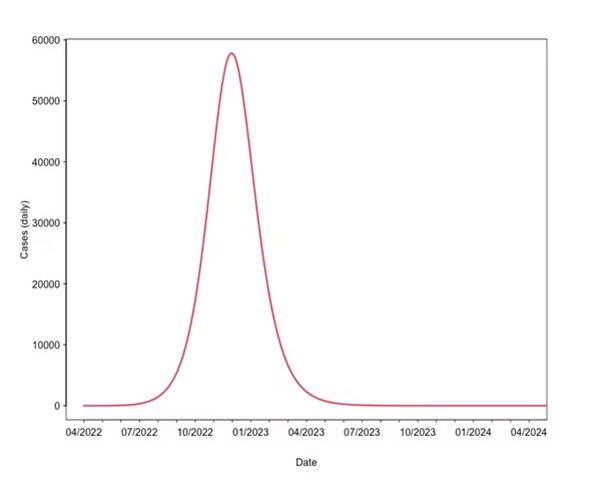
Scenario two assumes that everybody below the age of 50 is susceptible to the infection, reflecting the end of compulsory smallpox vaccination in the 1970 and 1980s. The virus will continue spreading, effectively searching for pockets of high-risk and non-immune communities.
Unless a combination of contact tracing and ring vaccination stops the spread, monkeypox will continue spreading. But, given the low transmissibility of monkeypox, the epidemic may fizzle out before reaching the herd immunity threshold of 50 per cent of the population.
Scenario three: becoming endemic
Complete eradication is impossible because monkeypox exists in a wide range of animal hosts. The low transmissibility also means it can survive at low levels in the population. In addition, the long incubation period and variable symptoms allow it to avoid detection. Therefore, monkeypox may have already been spreading for a long time.
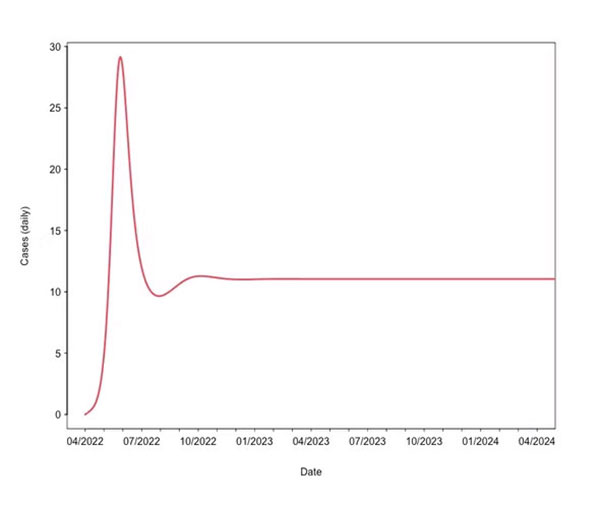
In scenario three, following the large outbreak, the disease will settle on a long-term, relatively constant level. Similar to the pre-vaccination smallpox or chickenpox.
The influx of susceptible people through birth or migration will keep the virus in the population. Mass vaccination programs might be needed to eradicate the disease. But relatively low monkeypox transmissibility means such programs are likely to be highly effective.
Scenario four: recurrent large epidemics
The current epidemic might be the first instance of a series of outbreaks. In the long term (scenario four), we should expect a return of monkeypox caused by future “zoonotic events” where the disease jumps from animal hosts to humans. As the cross-immunity from smallpox vaccines wanes, the epidemics can become even more substantial.
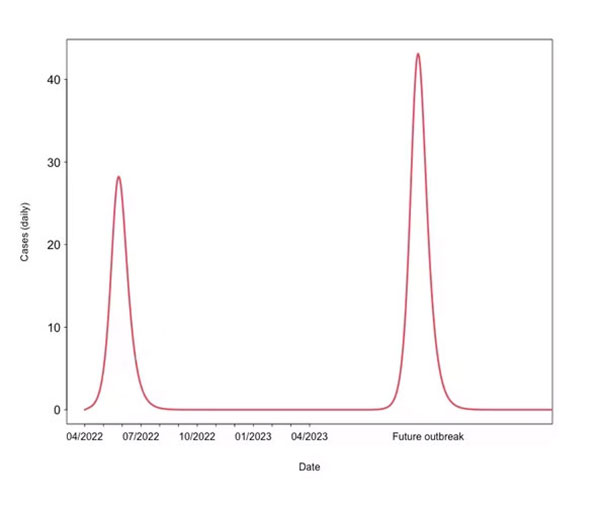
Little is known about the potential of monkeypox to mutate. Still, there is potential for it to evolve into a more rapidly spreading variant.
Vaccines for monkeypox exist and are about 85 per cent effective. Although there are currently not enough doses to vaccinate everyone, there is no need for a mass-vaccination program given monkeypox’s low transmissibility. Instead, vaccines should be offered to those most at risk, including communities in Africa most in contact with the wild animals that carry the virus.![]()
![]()
Read more: Health, Science + Tech















Tyee Commenting Guidelines
Comments that violate guidelines risk being deleted, and violations may result in a temporary or permanent user ban. Maintain the spirit of good conversation to stay in the discussion.
*Please note The Tyee is not a forum for spreading misinformation about COVID-19, denying its existence or minimizing its risk to public health.
Do:
Do not: